Functional electrical stimulation, FES, in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) is defined as the electrical stimulation of muscles that have impaired motor control, in order to produce a contraction to obtain functionally useful movement. It was first proposed in the 1980s as a treatment option in children with cerebral palsy (CP).

Marietta van der Linden, Queen Margaret University – Rehabilitation Sciences, Edinburgh UK, August 28, 2012
FES is used to achieve a direct orthotic effect during gait, for example, by triggering the dorsiflexors to lift the foot in swing or to trigger the quadriceps to extend knee in stance. Probably the most common application, at least in the adult stroke population, is FES applied to the dorsiflexors during the swing phase to prevent drop foot which could lead to tripping and falls.
A 2009 UK National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidance states that current evidence on safety and efficacy of FES for improving drop foot of central neurological origin is adequate to support the use of this procedure. However, the studies reviewed for this guidance were mainly on the adult stroke population.
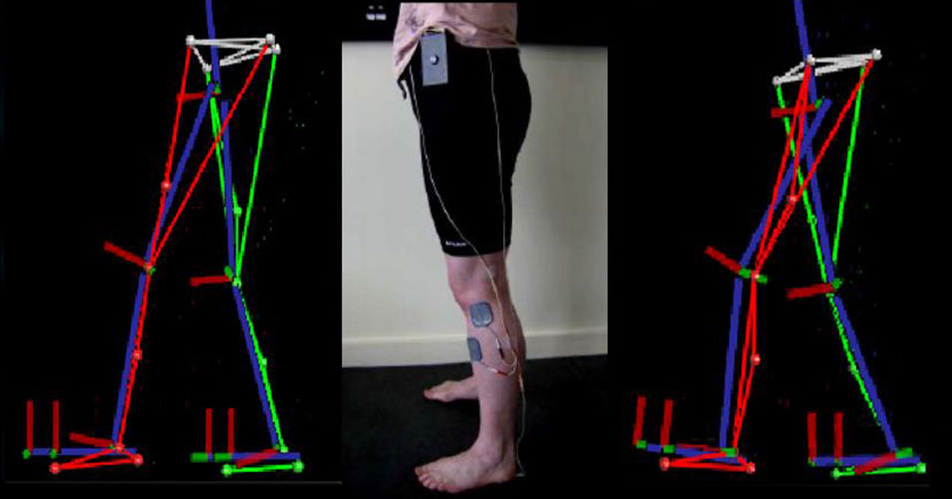
Putting Your Worst Foot Forward – Using Electrical Stimultion to Improve Walking in People with Stroke Cerebral palsy and MS. Queen Margaret University
Currently, ankle foot orthoses (AFOs) are most commonly prescribed for children with CP with insufficient dorsiflexion in the swing phase (drop foot), although as also discussed in the literature, children often dislike wearing them. In addition, AFO use is also often associated with weakness and atrophy of the lower limb muscles and this may lead to a poorly developed foot structure.
A recent review with regard to electrical stimulation for children with CP only found five small-scale studies with 12 participants or less. Only two studies used gait analysis to quantify the change in gait kinematics due to the application of FES. As a result, recent reviews called for appropriately powered studies with more rigorous research designs into the effects of FES in children with CP.

| WalkAide is a lightweight, single-unit device worn below the knee, fully operable with one hand. Children have the freedom to choose to walk with or without footwear, up and down the stair and even sidestep. |
The research by Prosser et al., is therefore an important addition to the evidence for FES of the tibialis anterior muscle in children and adolescents with CP. Nineteen participants enrolled in this study, and a statistically significant improvement of dorsiflexion during swing was found with FES. In addition, the authors report clinically relevant information such as the average time the device was used and how many participants continued to use the device after 3 months (18/19).
| Professor Marietta van der Linden (MSc, PhD) is a Senior Research Fellow in the Dietetics, Nutrition & Biological Sciences, Physiotherapy, Podiatry & Radiography Division. She is also co-director of Centre for Health, Activity and Rehabilitation Research (CHEARR) |
 Source Queen Margaret University
Source Queen Margaret University
| References |
Functional electrical stimulation in children and adolescents with cerebral palsy, Marietta van der Linden, Queen Margaret University – Rehabilitation Sciences, Edinburgh UK, 2012, First published online August 28, 2012. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 54: 972. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2012.04419.x
| Further reading |
A systematic review and meta-analysis of neuromuscular electrical stimulation post-botulinum toxin injection in children with cerebral palsy. Yang FA, Mi Le JR, Lu CH, Huang CC, Chen HC. Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 8;15(1):4690. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88991-5.
Advances in neuroprosthetic management of foot drop: a review, Gil-Castillo J, Alnajjar F, Koutsou A, Torricelli D, Moreno JC. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2020 Mar 25;17(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12984-020-00668-4. Full text, PDF
The orthotic and therapeutic effects following daily community applied functional electrical stimulation in children with unilateral spastic cerebral palsy: a randomised controlled trial, Pool D, Valentine J, Bear N, Donnelly CJ, Elliott C, Stannage K. BMC Pediatr. 2015 Oct 12;15:154. doi: 10.1186/s12887-015-0472-y. Full text, PDF
Habitual functional electrical stimulation therapy improves gait kinematics and walking performance, but not patient-reported functional outcomes, of people with multiple sclerosis who present with foot-drop, van der Linden ML, Hooper JE, Cowan P, Weller BB, Mercer TH. PLoS One. 2014 Aug 18;9(8):e103368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103368. Full text, PDF
Also see
Putting Your Worst Foot Forward – Using Electrical Stimultion to Improve Walking in People with Stroke Cerebral palsy and MS Queen Margaret University
Functional Electrical Stimulation Cerebral Palsy Guidance
